Your on-line source for reliable and unbiased information about the evaluation & treatment of heart disease.
The aorta is the major blood vessel that arises from the left ventricle and is separated from it by the aortic valve. The left main coronary artery arises from above the left portion of the aortic valve and then usually divides into two branches, known as the left anterior descending (LAD) and the circumflex (Circ) coronary arteries. In some patients, a third branch arises in between the LAD and the Circ. This is known as the ramus (pronounced ray-muss), intermediate , or optional diagonal coronary artery.
The LAD travels in the groove (known as the inter-ventricular groove) that runs in the anterior or front portion the heart. It sits between the right and the left ventricles or the two lower chambers of the heart.
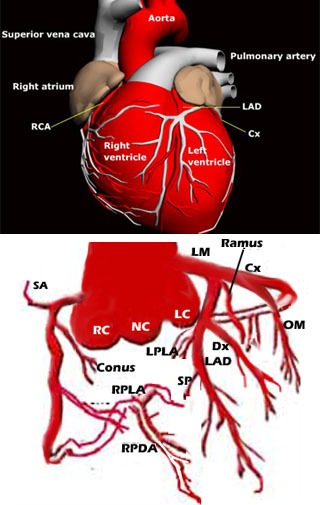
The LAD gives rise to the following two sets of branc hes:
- The diagonals are branches of the LAD that runs diagonally away from the LAD and towards the left edge in front of the heart.
- The septal perforators (SP) runs into the septum (partition that separates the two ventricles) and provides its blood supply.
![]()
©1999-2017, 20XXA.S.M. Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved, including design and all graphic contents & animations


